Coffee is one of the most complex beverages in the world, containing more than a thousand chemical compounds that contribute to its distinctive taste and aroma. These compounds are formed through natural growth, post-harvest processes, and roasting, making every cup of coffee a unique sensory experience.
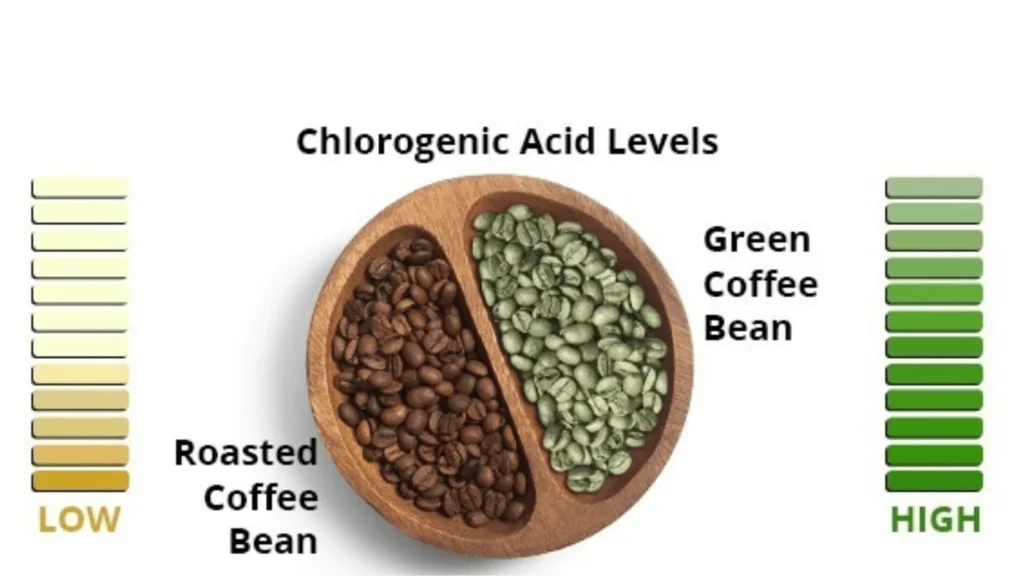
One of the most important elements in coffee is caffeine, which not only provides a stimulating effect but also adds a slight bitterness to the cup. Another key group of compounds is chlorogenic acids, which affect acidity and body, shaping the balance between sharpness and smoothness.
During roasting, chemical reactions such as the Maillard reaction produce volatile compounds that give coffee its signature aroma, ranging from fruity and floral to nutty or chocolaty notes. In addition, lipids and carbohydrates play a role in creating texture and mouthfeel, while proteins influence both flavor stability and crema in espresso.
The unique combination of these compounds explains why coffee from different origins, such as Sumatra, Java, or Lampung, can deliver remarkably different taste profiles. Understanding these natural components not only enriches the appreciation of coffee but also helps producers and exporters like PT Dua Putra Sekincau maintain quality and consistency for international markets.





